ABOUT LINUX MINT
Linux Mint is an operating system for desktop and laptop computers. It is designed to work 'out of the box' and comes fully equipped with the apps most people need.
Linux Mint is a community-driven Linux distribution based on Ubuntu. There is also LMDE, which stands for "Linux Mint Debian Edition", an alternative version based on Debian.
Linux Mint’s release schedule follows that of Ubuntu’s LTS releases. Linux Mint releases come out a few months after the corresponding Ubuntu LTS release because the Linux Mint team needs time for their own development and testing work. Each Linux Mint release is supported for five years, which is the same as the corresponding Ubuntu LTS release.
DESKTOP ENVIRONMENT AKA EDITION OR FLAVOR
A Linux desktop environment is a graphical user interface (GUI) that provides a collection of tools, applications, and settings to make the Linux operating system more accessible and user-friendly for most individuals. Popular examples include GNOME, KDE Plasma, XFCE, MATE, COSMIC and Cinnamon. These environments offer varying degrees of customization, performance, and functionality, allowing users to choose the one that best suits their preferences and needs.
Cinnamon Edition | Sleek, modern, innovative ⭐️
This is the edition on which this guide is based on, we highly recommend it for Windows users.
The most popular version of Linux Mint is the Cinnamon edition. Cinnamon is primarily developed for and by Linux Mint. It is slick, beautiful, and full of new features.

MATE Edition | Stable, robust, traditional
Linux Mint is also involved in the development of MATE, a classic desktop environment which is the continuation of GNOME 2, Linux Mint’s default desktop between 2006 and 2011. Although it misses a few features and its development is slower than Cinnamon’s, MATE runs faster, uses fewer resources and is more stable than Cinnamon.

Xfce Edition | Light, simple, efficient
Xfce is a lightweight desktop environment. It doesn’t support as many features as Cinnamon or MATE, but it’s extremely stable and very light on resource usage.

Debian Edition | An alternative to Ubuntu (for advanced users)
LMDE aims to be as similar as possible to Linux Mint, but without using Ubuntu. The package base is provided by Debian instead.
Its goal is to ensure Linux Mint can continue to deliver the same user experience if Ubuntu was ever to disappear.

 INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION
Linux Mint Installation Guide can be found here:
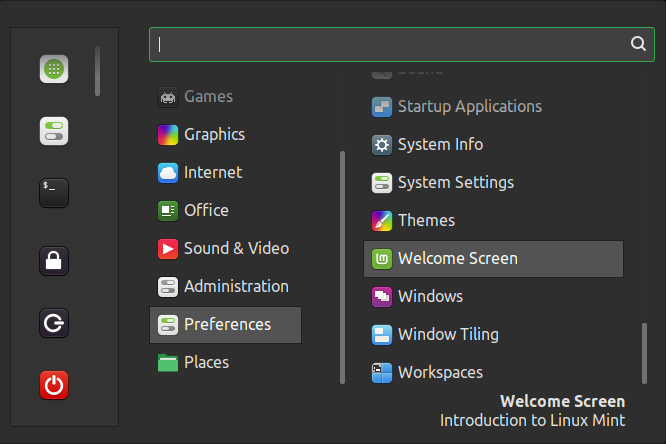
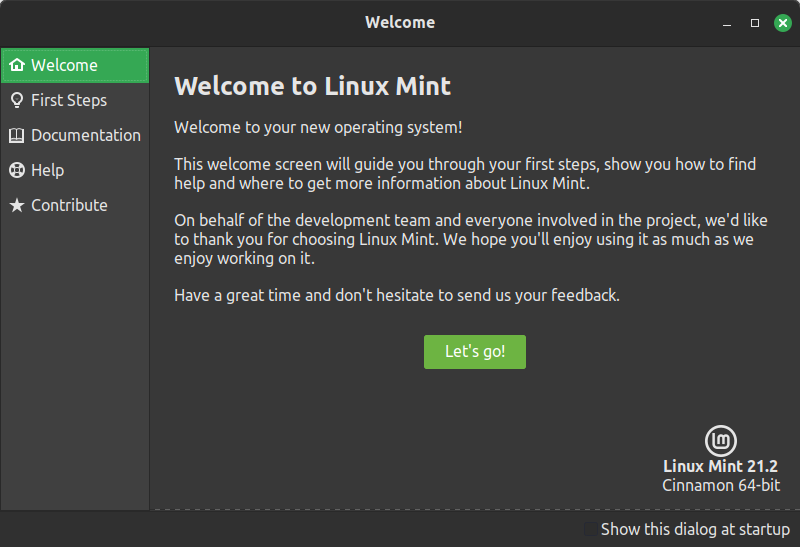
 WELCOME SCREEN
WELCOME SCREEN
The Welcome Screen guides you on your first steps on what you should do after a fresh installation of Linux Mint, like choosing your color theme, setting up System Snapshots, Check the drivers, the updates, enable the firewall, etc. You also have access to the links of the Documentation from the Welcome Screen.
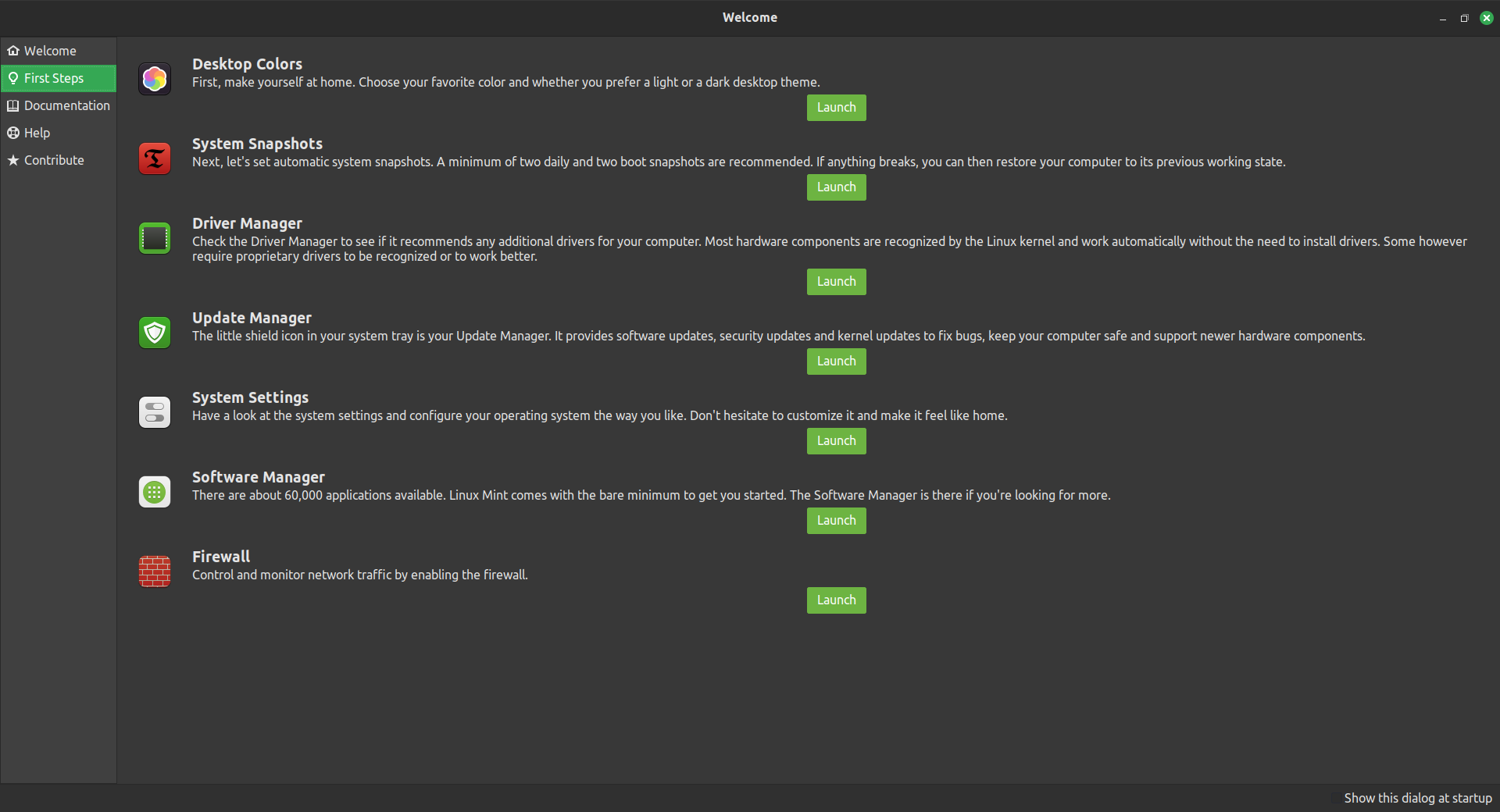
 SOFTWARE MANAGER
SOFTWARE MANAGER
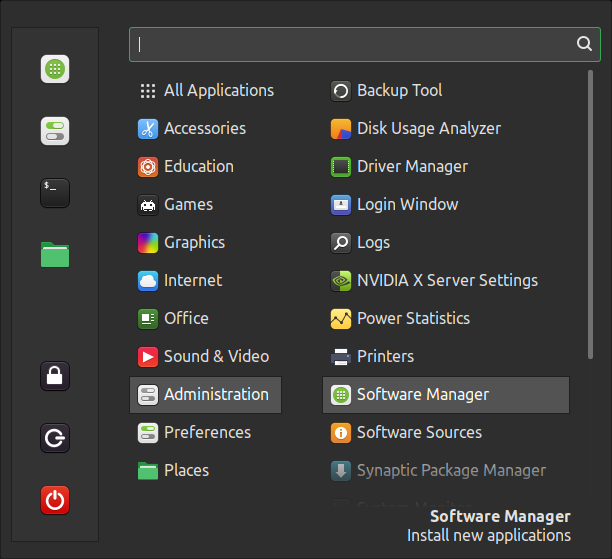
The Software Manager is your app store module, from where you search, install or remove your applications. Unlike Microsoft Windows you don't need to search on different websites to find your softwares, all is there in one place!

 UPDATE MANAGER
UPDATE MANAGER
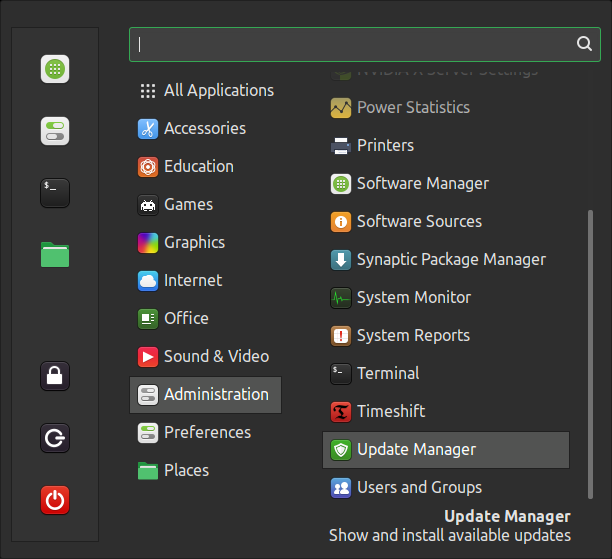
The Update Manager is the module from where you update softwares, packages and kernel.
You can follow the status of the updates at the bottom right of panel on your screen. It has a shield icon.
The shield icon has 3 states: ![]()
![]()
![]()
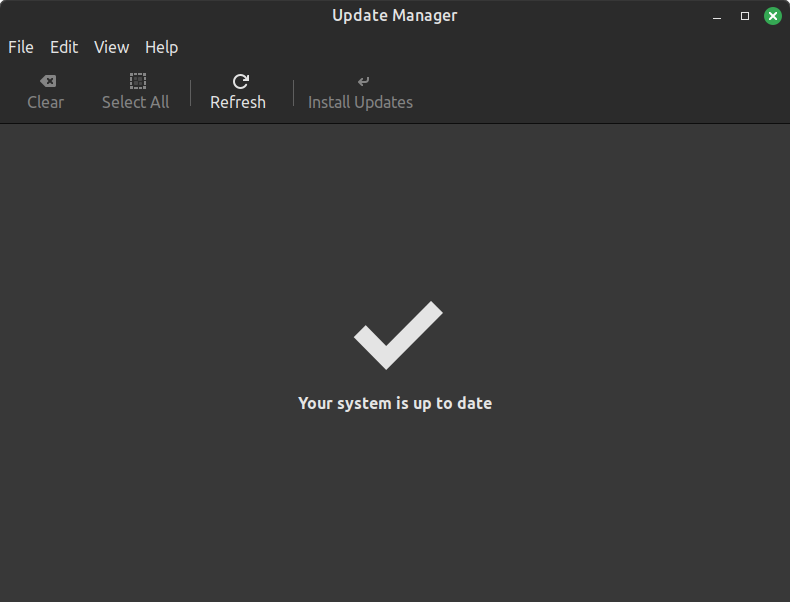
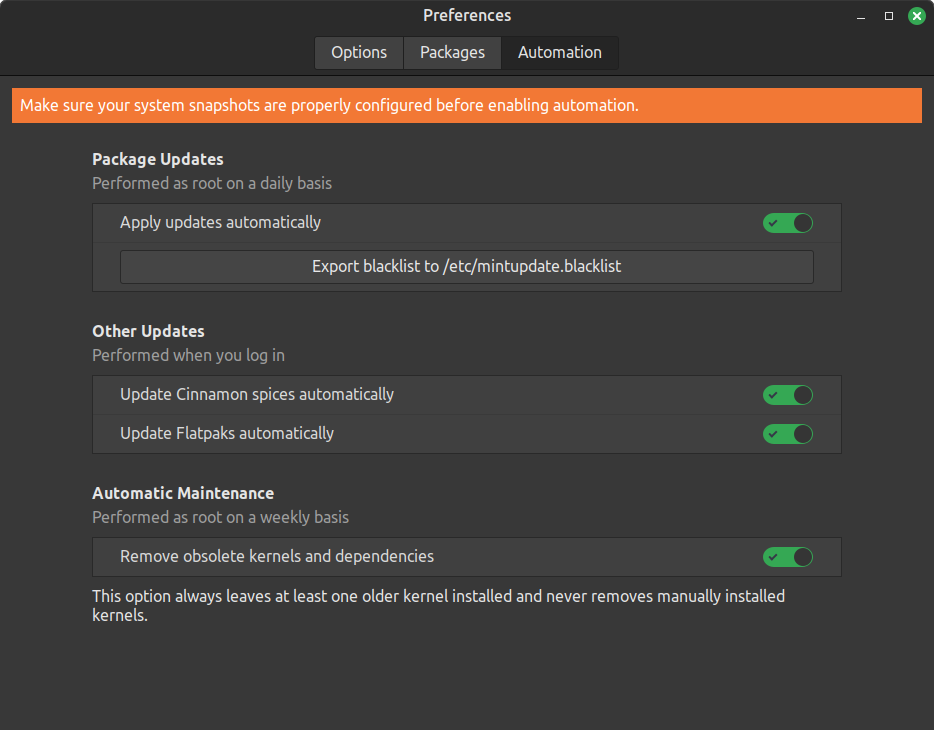
It is also possible to make the update and maintenance process fully automated if you wish. To do so, go to Edit → Preferences → Automation, then enable all the options.
⚠️ It is highly recommended to have your system snapshots properly configured before you enable this mode.
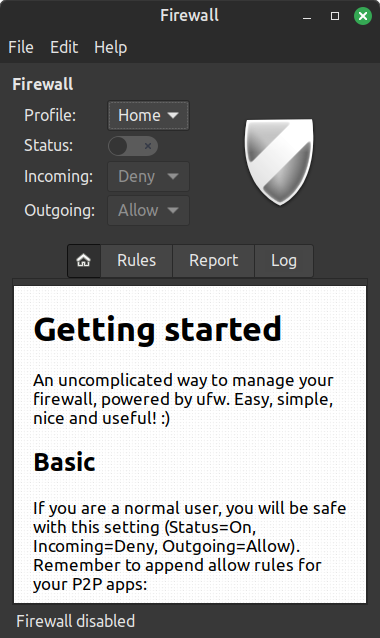
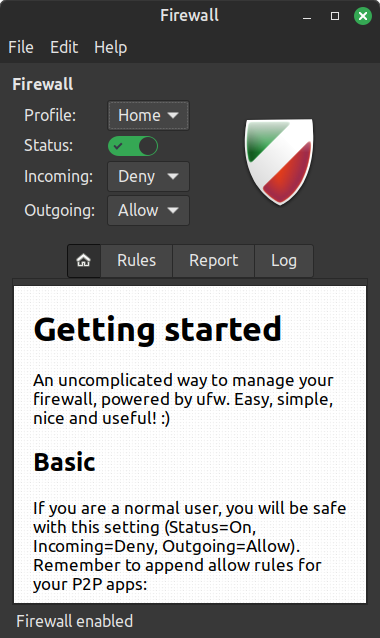
 FIREWALL
FIREWALL
The Firewall will help you to secure the network traffic. By default it is not enabled, to turn it on, you just need to click the Status switch and that is all you need to do, for a normal home user.
💡️ TIPS AND TRICKS
Here are few tips and trick you may find useful.
Date and Time format
You can customize the clock format like you wish!
To do so, you need to right-click on the clock/calendar applet in the bottom-right corner, then click “Configure”, in the calendar settings, enable the “Use a custom date format”. In Date format you can now type soemthing like this exemple: %a %d-%m-%y %H:%M:%S
More info on the syntax here.
Enable touchpad gestures for laptops
You can enable the touchpad gestures, this is very useful for laptops.
To do so, follow this path : Menu → Preferences → Gestures → Settings → Enable gestures.
Configure the actions in the Swipe and Pinch tabs.
Protect your eyes with Night Light (Mint 22.1 Cinnamon)
Night Light is a feature designed to reduce your exposure to blue light by warming up the color of your monitor. As you approach bedtime, it adjusts the screen to help reduce eyestrain, headaches, and improve sleep quality.
This feature is fully integrated into the Cinnamon desktop environment and it supports both Xorg and Wayland.
To enable Night Light, navigate to Settings → Night Light and toggle the option to activate it.
By default, Cinnamon automatically calculates your local sunrise and sunset times based on your system's timezone. During the day, the screen displays cooler, bluer tones, while at night, Night Light shifts the screen to warmer, redder tones.
If you prefer, you can switch to a manual schedule and set custom start and end times for when the feature is active.
You can also adjust the color temperature to control how warm or neutral you want the display to be during the night.
Get the latest Nvidia proprietary GPU Drivers
Linux Mint’s repository does not have the latest Nvidia driver by default. This is because the Linux Mint team does not automatically push the latest Nvidia drivers to their repository for general users. Instead, they rely on the open-source Nouveau driver, which is sufficient for general use but may not provide optimal performance for gaming and high-resolution video playback.
For users who need the latest Nvidia driver, add the Personal Package Archive (PPA) from “Graphics Drivers” team.
Adding the PPA to your system:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:graphics-drivers/ppa
sudo apt update
Search available driver:
sudo apt search nvidia-driver
Install the latest driver (ex: nvidia-driver-555):
sudo apt install nvidia-driver-555
sudo apt update
Reboot your system:
sudo reboot
Game compatibility
Increase vm.max_map_count
Having the vm.max_map_count set to a low value can affect the stability and performance of some games. It can therefore be desirable to increase the size permanently by creating the following sysctl config file.
Create de config file:
sudo nano /etc/sysctl.d/80-gamecompatibility.conf
copy this line in the new created config file: vm.max_map_count = 2147483642
Save and close nano.
Apply the changes without reboot by running:
sudo sysctl --system
source: Arch Wiki
Mainline Kernel
⚠️ Be sure you know what you are doing! Create a backup (with Timeshift) before you change your kernel, you could get compatibility issues!
Go to the Ubuntu Mainline Kernel page and choose to the version you want.
For AMD/Intel CPUs, simply download the first 4 .deb packages from the web page.
If you don’t know your CPU architecture type, open terminal (Ctrl+Alt+T) and run either uname -m or dpkg --print-architecture command to tell.
After downloaded the corresponding .deb packages, right-click on blank area in your downloads folder and select "Open in Terminal". Finally, run the command sudo apt install ./*.deb or dpkg -i *.deb to install all the .deb packages in that folder.
When done, reboot your computer and run command uname -r to identify your kernel version.
If you encounter issues with the Linux kernel and want to revert to default kernel or another installed kernel, follow these steps:
- Boot your computer.
- Press the Esc key during startup to access the boot menu.
- Select "Advanced options" from the boot menu.
- Choose a different kernel version from the list of available kernels.
A better kernel for gaming
XanMod is a general-purpose Linux kernel distribution with custom settings and new features. Built to provide a stable, smooth and solid system experience.
Liquorix is an enthusiast Linux kernel designed for uncompromised responsiveness in interactive systems, enabling low latency compute in A/V production, and reduced frame time deviations in games.
linux-tkg The Linux-TKG (Tweaked Kernel for Gaming) is not a kernel itself but a build system for the Linux kernel that allows users to choose and apply various patches and configurations.
🔗️ LINKS
Various links to guides, articles and infos about Linux Mint.
- 8 Reasons Why Linux Mint is Better Than Ubuntu for Linux Beginners
- 10 Things to Do First in Linux Mint 21.1 Cinnamon
- Linux Filesystem Hierarchy
by A1RM4X
- How to optimize Linux Mint for gaming - Ultimate Full Tutorial - Linux Switching series - Part 5
- Gaming on LMDE 7? Wayland vs X11, Performance & Backports Explained